- HOME
- About Us
- Mandatory Disclosures
- COURSES
- Campus Life
- Gallery
- Blogs
- Events
- Contact
Computer Networking: OSI Model
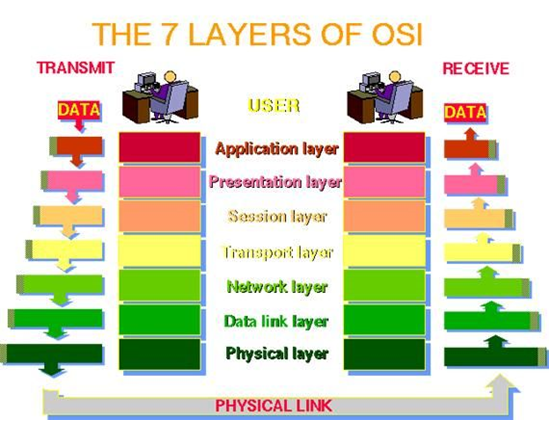
Open System Interconnection model is foundation for all communications that take place between computers. The main purpose of this model is to allow communication between different systems.
Example: Apple Macintosh is directly communicate with any other device like IBM computers with the help of OSI model.
There are seven layer in this model.
1. Physical Layer
2. Data link Layer
3. Network Layer
4. Transport Layer
5. Session Layer
6. Presentation Layer
7. Application Layer
Seven Layers are organized in subgroups :
Network Support Layers :
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
User Support Layer
Session Layer
Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Data transmission Layer:
Transport layer
Layers in OSI Model
Physical Layer: This layer is responsible for actual physical connection between the devices. Such as physical connection may be made by using twisted pair cable, fiber optic, coaxial cable or wireless communication media.
Functions of Physical Layer
Transmission bits into signals.
Bit synchronization
Bit rate control
Line Configuration
Data Link Layer: Data link layer is responsible for converting data stream into signals and send over underlying hardware. At the receiving end, Data link layer picks up data from physical layer in the form of electrical signals and hands over to network layer.
Functions of Data Link Layer
Framing
Addressing
Error control
Flow control
Network Layer: This layer is responsible for convert the data into packet and also responsible for routing packets from source to destination within and outside the subnet.
Functions of Network Layer:
Routing
Logical Addressing
Transport Layer: Transport layer offers peer-to-peer and end-to-end connection between two remote hosts. Transport layer takes data from upper layer (i.e. Application layer) and then breaks it into smaller size segments.
Main Protocol of Transport Layer:
Transmission Control Protocol
User Datagram Protocol
Creating a connection involves three steps:
Connection establishment
Data transfer
Connection Release
Functions of Transport Layer
Segmentation of message into packet and reassembly of packets into message.
Connection management
Service point addressing
Flow control
Error control
Session Layer: Session layer is fifth layer of OSI model.
Session layer has the primary responsibility of beginning, maintaining and ending the communication between two devices, which is called session.
Functions of Session Layer
Establishment, maintaining and ending a session.
Dialog control
Dialog separation
Presentation Layer: Presentation layer is sixth layer of OSI model. This layer is concerned with syntax and semantics of information exchanged between devices.
Functions of Presentation Layer:
Data presentation and translation
Data encryption
Data compression
Application Layer: This layer is topmost layer of OSI model.
It enables the user, whether humans or software, to access the network by providing user interface. This layer provide services that directly support user application such as database access, e-mail and file transfer.
Functions of Application Layer:
Network Virtual Terminal
File transfer, access and management
Mail services
Designing a network in form of layer offers several benefits.
The various networking functions such as error detection, encryption, flow control, routing, multiplexing can be isolated into modules.
Separating the various functions into different modules make design process simpler and easier.
Such modules also enables us to do research and development on each layer independently from the other layers.

