- HOME
- About Us
- COURSES
- Campus Life
- Gallery
- Blogs
- Events
- Contact
ABOUT YOUR LIVER

Human liver is a largest organ. which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification & purification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemical reactions necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper side of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. Its other role is in metabolism. Liver is a only organ that has the ability to regenerate itself.
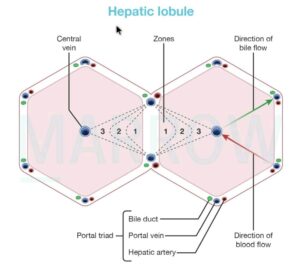
Structure of Liver
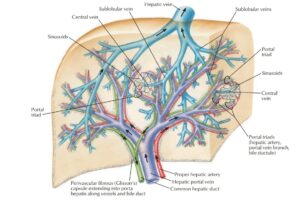
The liver is a bilobed, triangular structure consisting of a smaller left lobe and larger right lobe. The two lobes are separated by the falciform ligament. Liveris covered by a layer of fibrous tissue called Glisson’s capsule. This capsule is covered by peritoneum. This protects the liver from physical damage.
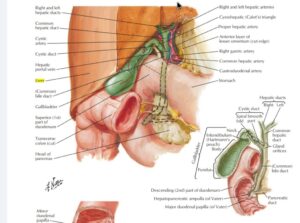
It has two main sources of blood:
Hepatic Portal Vein – the nutrient-rich blood Carryout from the digestive system
Hepatic Artery – The oxygenated blood carries from the heart.
Size & weight of Liver
- A human liver normally weighs approximately 1.5 kg
- width of about 15 cm (6 in).
- men 970–1,860 g (2.14–4.10 lb)
- women 600–1,770 g (1.32–3.90 lb)
Major Functions of Liver
The important functions of the liver are mentioned below:
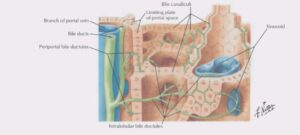
- Production of Bile
Bile, helps in the absorption & digestion of cholesterol, fats and vitamins is produced in the liver.
- Absorption of Bilirubin
Bilirubin is formed by the breakdown of hems present in hemoglobin. The iron is released & stored in the liver to make blood cells.
- Supporting Blood Clots
Vitamin K absorb by the Bile. If bile is not produced, then clotting factors will not be produced.
- Metabolization of Fats
Fats are broken down& digested by the help of bile’s.
- Carbohydrate Metabolization
Carbohydrates are stored in the liver as glycogen and they are broken down into glucose and released into the blood stream to maintain glucose levels.
- Storage of Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins are stored in liver like that A, D, E, K, and B12. Iron is also stored in the form of ferritin to form new red blood cells.
- Metabolization of Proteins
The digestion of proteins is possible by the helps of bile’s present in liver.
- Filtering Blood
The compounds like that hormones, alcohol, etc. are filtered by the liver from the blood.
- Immunological Function
Liver have Kupffer cells involved in immune activity. These destroy any disease-causing agents.
- Angiotensinogen Synthesis
This hormone is a responsible for narrowing of blood vessels which results in an increase in blood pressure.
- Regeneration of Liver
The liver has the ability to regrow or re-generate itself in all the vertebrates. In humans, regeneration takes 8-15 days. In mice, takes around 5-7 days.
- Signs Symptoms of a fatty liver
- Swelling in Abdominal area
- Enlarged blood vessels.
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice
- Urine colour dark yellow
- stool colourpale yellow
- Nausea or vomiting
- Chronic fatigue
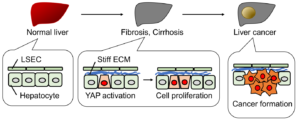
Liver Diseases
- Cirrhosis
This can be caused due to excess alcohol consumption, toxins and hepatitis. Here, in process of fibrosis the scar cells replace liver cells. The functionality of liver cells is destroyed, which might lead to liver failure.
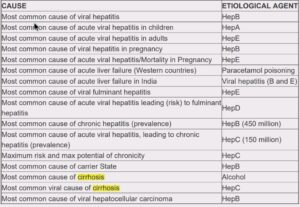
- Hepatitis
It is the inflammation of the liver is caused by viruses such as a hepatitis A, B and C. most cases
- Alcoholic Liver Disease
Excess of alcohol consumption leads to liver damage. It is the most common cause of liver cirrhosis.
- Liver Cancer
Alcohol and hepatitis are the major causes of liver cancer or liver carcinoma hepatocellular carcinoma is the type of liver cancer.
Laboratory Diagnosis of liver
- Biochemical diagnosis
- Bilirubin
- Direct
- Indirect
- SGOT
- SGPT
- Pathological investigation
- HCV Elisa
- Hbbsag Elisa
- liver biopsy
- Radiological
- Ultrasound
- Fibro scan
Dietary modifications for healthy liver
- AVOID ALCHOHAL
- AVOID RED MEAT / EXCESSIVELY FRIED MEAT
- AVOID PROLONGED FASTING AS IT STARTS GLUCONEOGENESIS IN BODY CAUSING PRODUCTION OF FREE RADICALS CAUSING DAMAGE TO LIVER PARENCHYMA
- FOOD BENEFICIAL FOR LIVER
- Tomato
- Pumpkin
- Banana
- Watermelon
- Salmon
- Tuna
- Avocado
- Mung Beans
- Papaya
- Grapes

